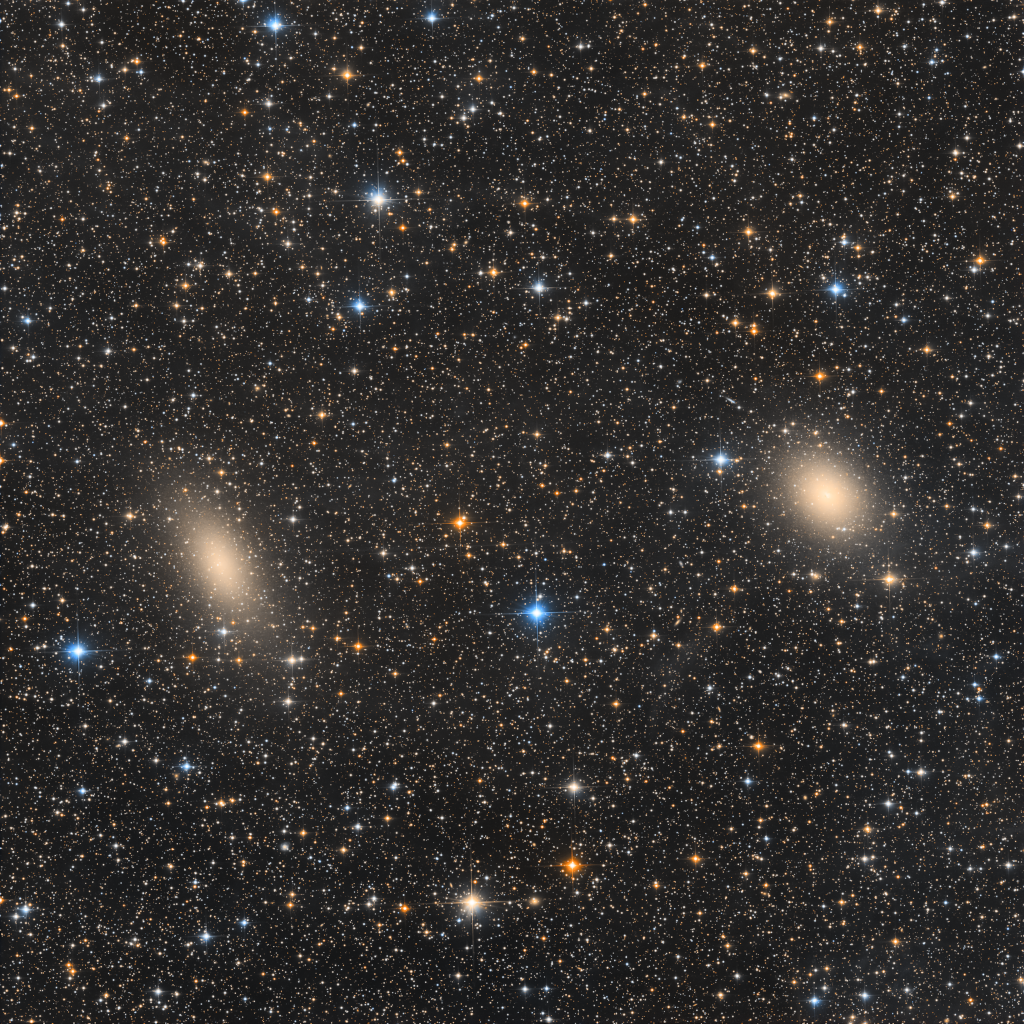

NGC 147 and NGC 185
Dwarf galaxies NGC 147 (left) and NGC 185 stand side by side in this deep telescopic portrait. The two are not-often-imaged satellite galaxies of M31, the great spiral Andromeda Galaxy, some 2.5 million light-years away. Their separation on the sky, less than one degree across a pretty field of view toward the constellation Cassiopeia, translates to only about 35 thousand light-years at Andromeda's distance, but Andromeda itself is found well outside this frame. Brighter and more famous satellite galaxies of Andromeda, M32 and M110, are seen much closer to the great spiral. NGC 147 and NGC 185 have been identified as binary galaxies, forming a gravitationally stable binary system. But recently discovered faint dwarf galaxy Cassiopeia II also seems to be part of their system, forming a gravitationally bound group within Andromeda's intriguing population of small satellite galaxies.
Read more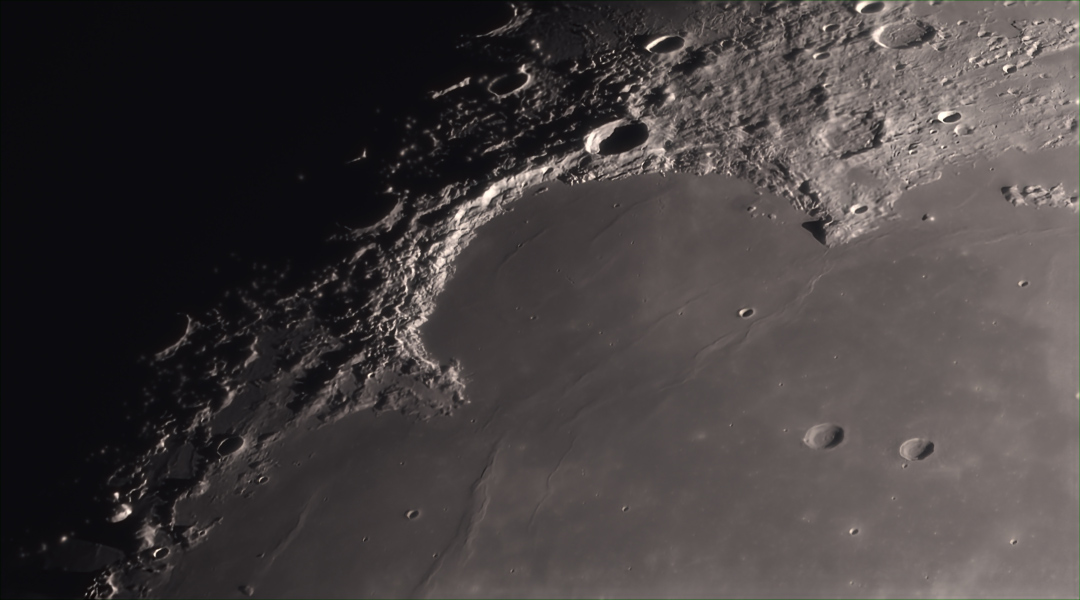
The Bay of Rainbows
Dark, smooth regions that cover the Moon's familiar face are called by Latin names for oceans and seas. That naming convention is historical, though it may seem a little ironic to denizens of the space age who recognize the Moon as a mostly dry and airless world, and the smooth, dark areas as lava-flooded impact basins. For example, this telescopic lunar vista, looks over the expanse of the northwestern Mare Imbrium, or Sea of Rains and into the Sinus Iridum, the Bay of Rainbows. Ringed by the Jura Mountains (montes), the bay is about 250 kilometers across. Seen after local sunrise, the mountains form part of the Sinus Iridum impact crater wall. Their rugged sunlit arc is bounded at the top by Cape (promontorium) Laplace reaching nearly 3,000 meters above the bay's surface. At the bottom of the arc is Cape Heraclides, depicted by Giovanni Cassini in his 1679 telescope-based drawings mapping the moon, as a moon maiden seen in profile with long, flowing hair.
Read more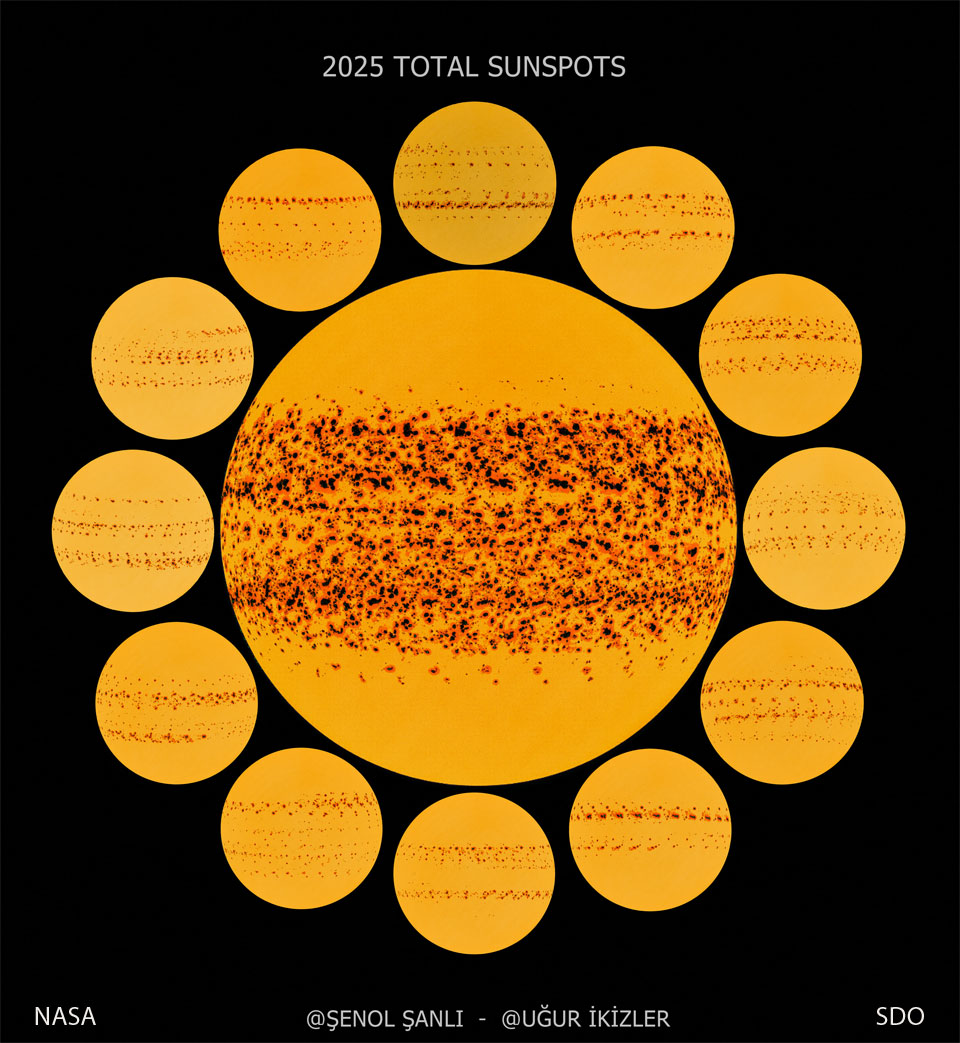
A Year of Sunspots
How many sunspots can you see? The central image shows the many sunspots that occurred in 2025, month by month around the circle, and all together in the grand central image. Each sunspot is magnetically cooled and so appears dark -- and can last from days to months. Although the featured images originated from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, sunspots can be easily seen with a small telescope or binoculars equipped with a solar filter. Very large sunspot groups like recent AR 4366 can even be seen with eclipse glasses. Sunspots are still counted by eye, but the total number is not considered exact because they frequently change and break up. Last year, 2025, coincided with a solar maximum, the period of most intense magnetic activity during its 11-year solar cycle. Our Sun remains unpredictable in many ways, including when it ejects solar flares that will impact the Earth, and how active the next solar cycle will be.
Read more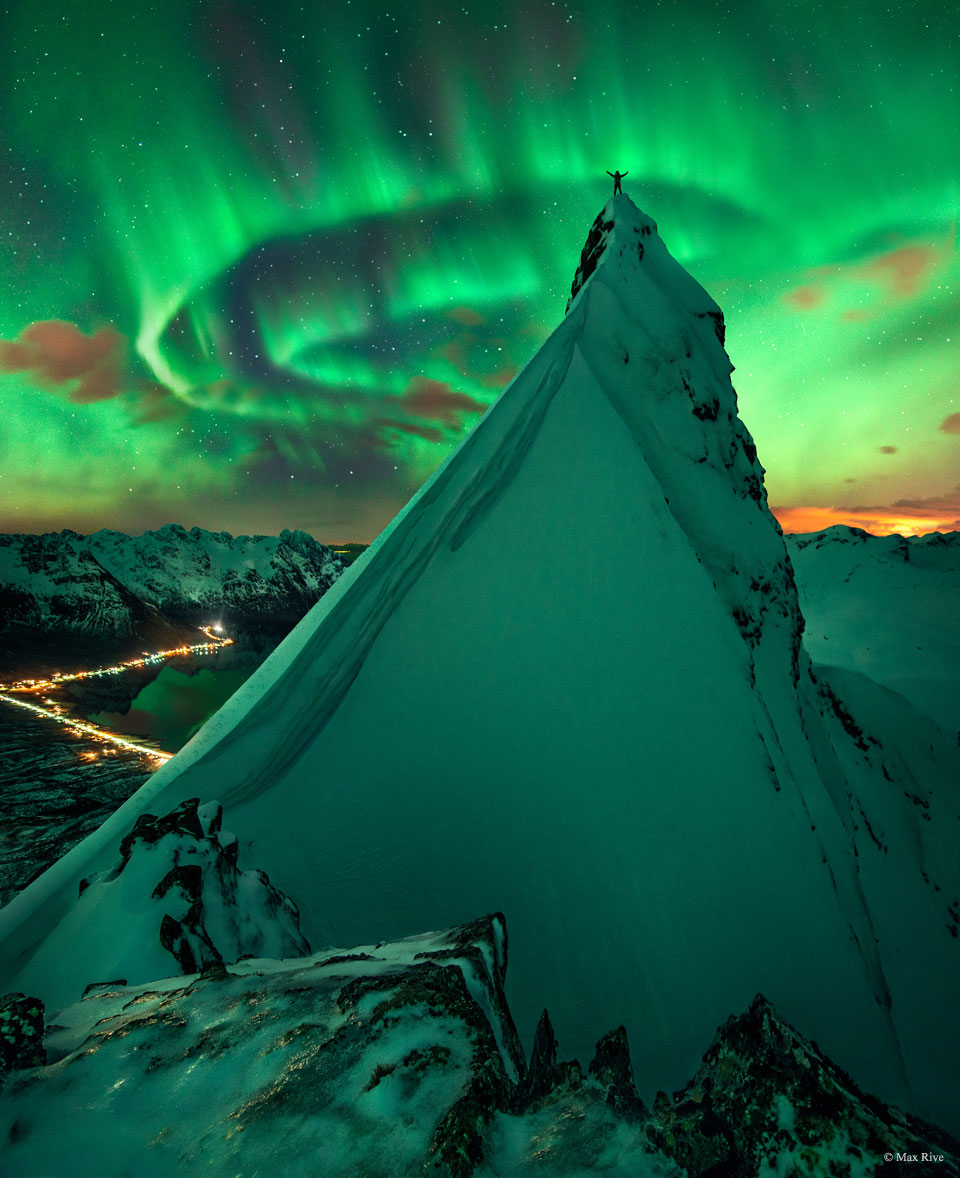
In Green Company: Aurora over Norway
Raise your arms if you see an aurora. With those instructions, two nights went by with, well, clouds -- mostly. On the third night of returning to same peaks, though, the sky not only cleared up but lit up with a spectacular auroral display. Arms went high in the air, patience and experience paid off, and the creative featured image was captured as a composite from three separate exposures. The setting is a summit of the Austnesfjorden (a fjord) close to the town of Svolvear on the Lofoten islands in northern Norway. The year was 2014. This year, our Sun is just passing solar maximum, the peak in its 11-year surface activity cycle. As expected, some spectacular auroras have recently resulted. Portal Universe: Random APOD Generator
Read more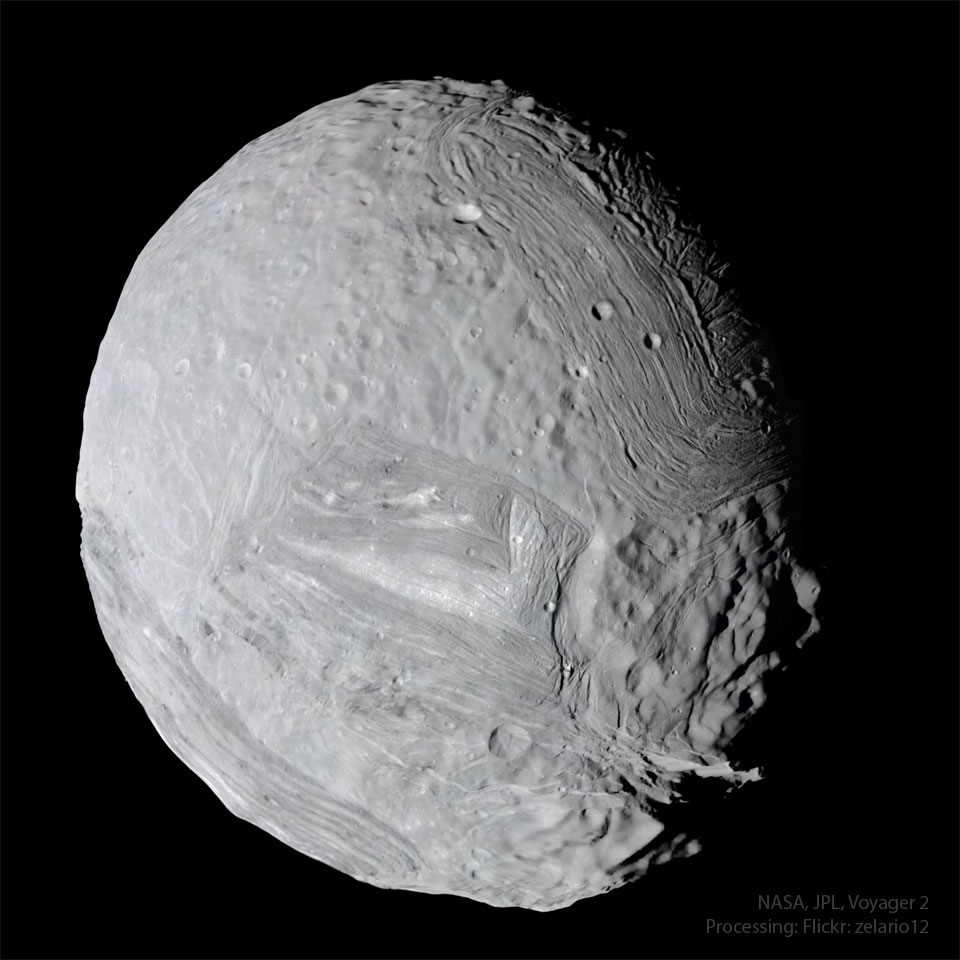
Miranda Revisited
What is Miranda really like? Visually, old images from NASA's Voyager 2 have been recently combined and remastered to result in the featured image of Uranus's 500-kilometer-wide moon. In the late 1980s, Voyager 2 flew by Uranus, coming close to the cratered, fractured, and unusually grooved moon -- named after a character from Shakespeare’s The Tempest. Scientifically, planetary scientists are using old data and clear images to theorize anew about what shaped Miranda's severe surface features. A leading hypothesis is that Miranda, beneath its icy surface, may have once hosted an expansive liquid water ocean which may be slowly freezing. Thanks to the legacy of Voyager 2, Miranda has joined the ranks of Europa, Titan, and other icy moons in the search for water, and, possibly, microbial life, in our Solar System. Jigsaw Moon: Astronomy Puzzle of the Day
Read more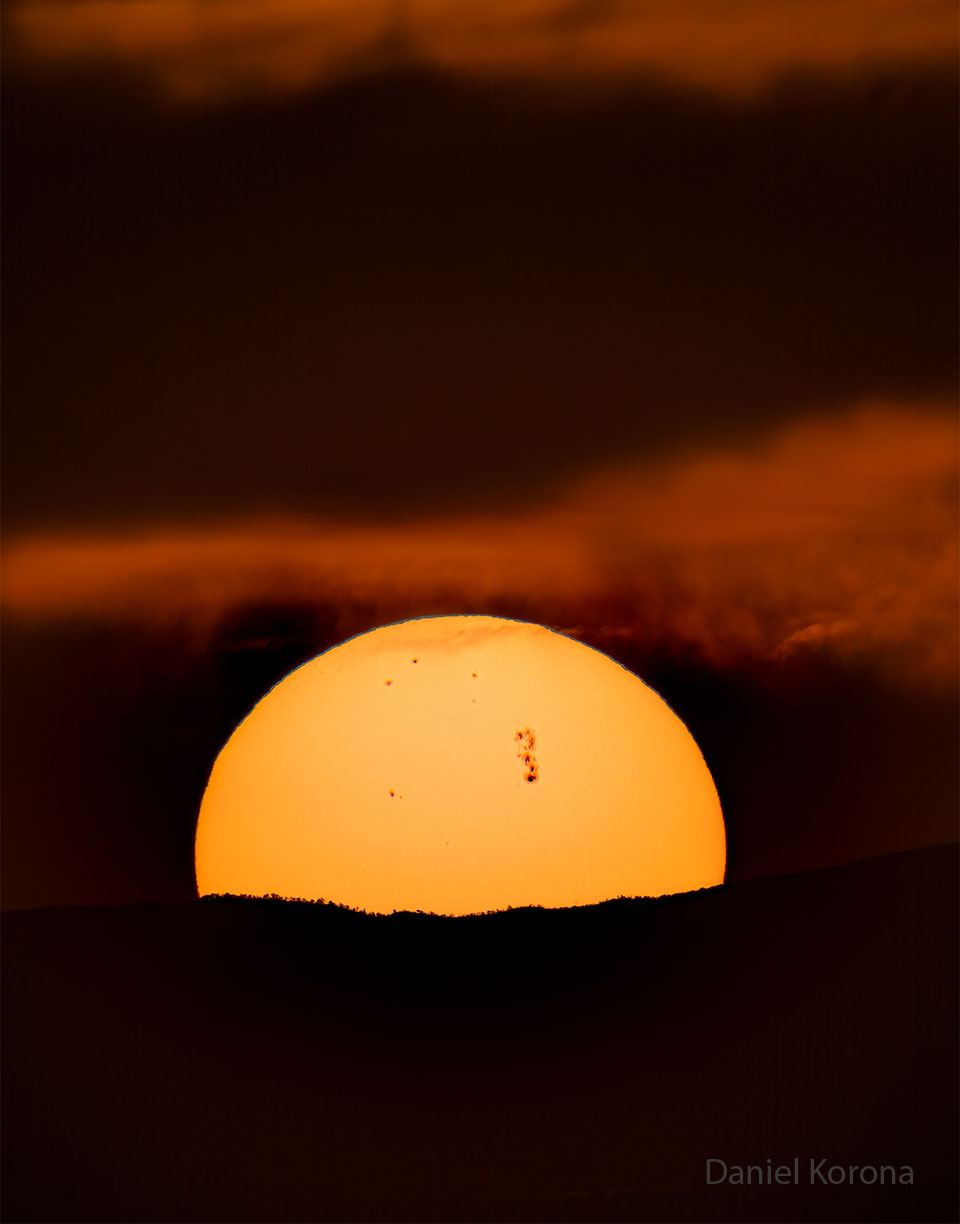
Active Sunspot Region 4366 Crosses the Sun
An unusually active sunspot region is now crossing the Sun. The region, labelled AR 4366, is much larger than the Earth and has produced several powerful solar flares over the past ten days. In the featured image, the region is marked by large and dark sunspots toward the upper right of the Sun's disk. The image captured the Sun over a hill in Zacatecas, Mexico, 5 days ago. AR 4366 has become a candidate for the most active solar region in this entire 11-year solar cycle. Active solar regions are frequently associated with increased auroral activity on the Earth. Now reaching the edge, AR 4366 will begin facing away from the Earth during the coming week. It is not known, though, if the active region will survive long enough to reappear in about two weeks' time, as the Sun rotates.
Read more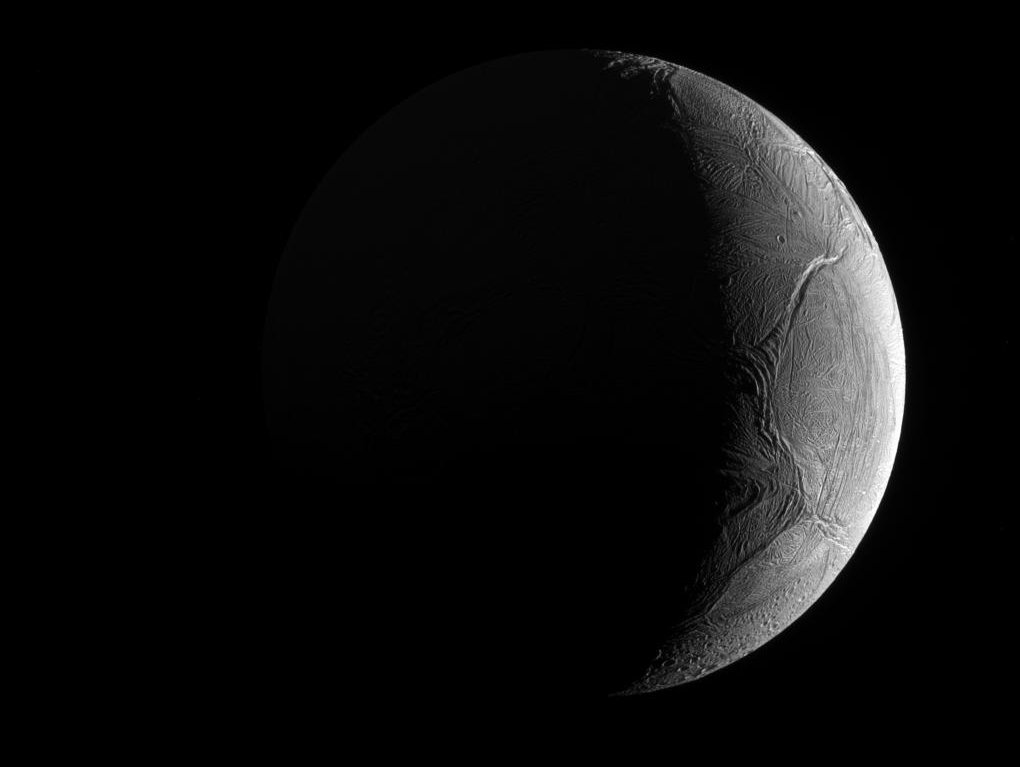
Crescent Enceladus
Peering from the shadows, the Saturn-facing hemisphere of tantalizing inner moon Enceladus poses in this Cassini spacecraft image. North is up in the dramatic scene captured during November 2016 as Cassini's camera was pointed in a nearly sunward direction about 130,000 kilometers from the moon's bright crescent. In fact, the distant world reflects over 90 percent of the sunlight it receives, giving its surface about the same reflectivity as fresh snow. A mere 500 kilometers in diameter, Enceladus is a surprisingly active moon. Data and images collected during Cassini's flybys have revealed water vapor and ice grains spewing from south polar geysers and evidence of an ocean of liquid water hidden beneath the moon's icy crust.
Read more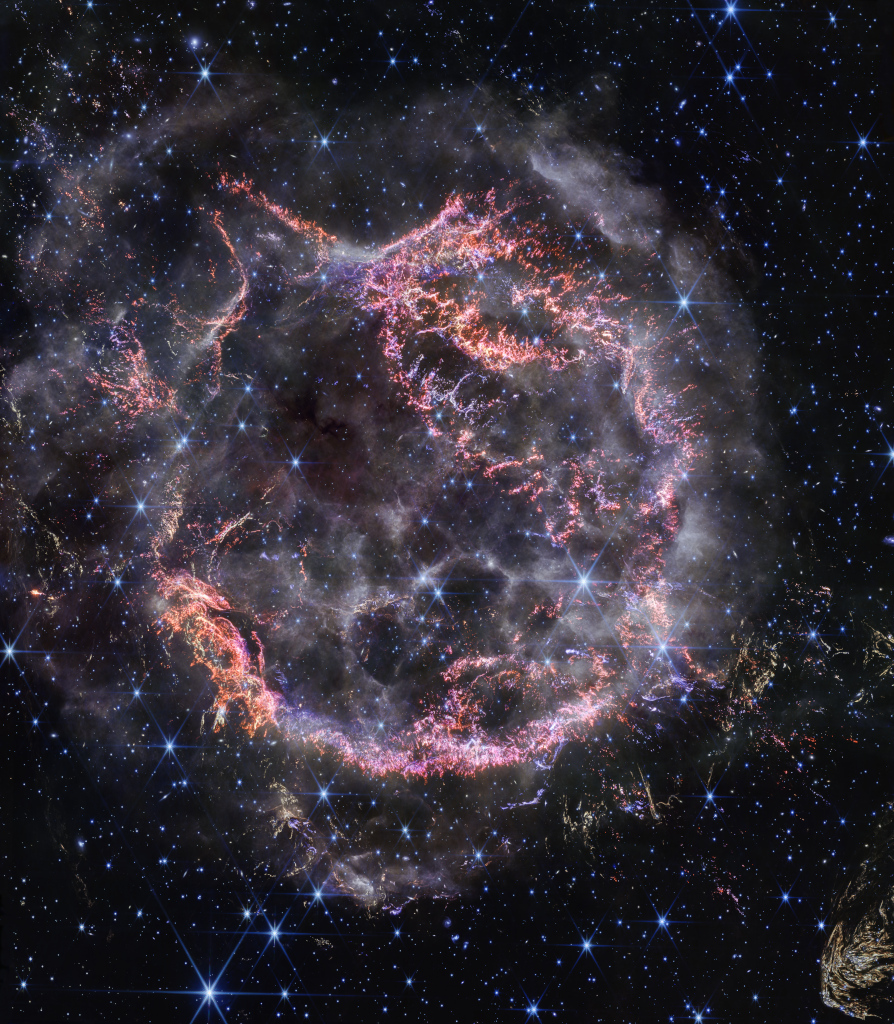
Supernova Remnant Cassiopeia A
Massive stars in our Milky Way Galaxy live spectacular lives. Collapsing from vast cosmic clouds, their nuclear furnaces ignite and create heavy elements in their cores. After only a few million years for the most massive stars, the enriched material is blasted back into interstellar space where star formation can begin anew. The expanding debris cloud known as Cassiopeia A is an example of this final phase of the stellar life cycle. Light from the supernova explosion that created this remnant would have been first seen in planet Earth's sky about 350 years ago, although it took that light 11,000 years to reach us. This sharp NIRCam image from the James Webb Space Telescope shows the still-hot filaments and knots in the supernova remnant. The whitish, smoke-like outer shell of the expanding blast wave is about 20 light-years across. A series of light echoes from the massive star's cataclysmic explosion are also identified in Webb's detailed images of the surrounding interstellar medium.
Read more